
Overview on CCUS
In the context of transition to carbon neutrality, emerging markets such as Carbon Capture, Utilization & Storage (CCUS) and geothermal are now essential to move towards low carbon energy sources, to activate energy efficiency levers and to participate in restoring forests or utilize carbon capture technology.
CCUS can be applied to a significant share of the emissions from heavy industries such as coal, waste incineration or natural gas. This market is linked to carbon pricing, which consists of implementing a tax or trading system to put a price on CO2 emissions. Carbon pricing has widely increased in the last years, both in coverage (see map) and in amount – it has increased to over 100€/ton CO2 in countries covered by the Emission Trading System (ETS) for the first time in 2023.
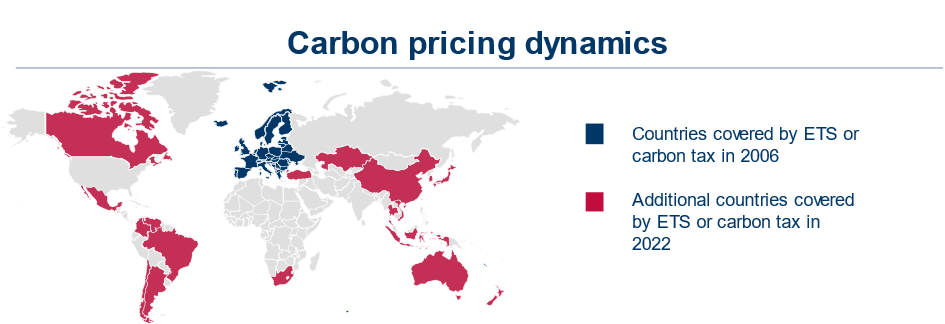
It becomes urgent to position oneself on the CCUS market
The CCUS market will see rapid growth in the coming decade: It reached $2.4B in 2022 and should reach $7.0B in 2030, at a 14.3% annual growth rate. 60% of today’s global CO2 is theoretically addressable by offset via CCUS technologies.
We are in the short period where subsidies will be set to cover investments over the coming decades. Several countries have recently enacted policies, and many subsidies are being released now to prepare for the future. For example, new integrated CCUS facilities projects announced in US and EU in the last three years include more than $27B investments.
It is the right moment to explore opportunities on the CCUS market, as the actors will leverage on those trends to strengthen their positioning.
CCUS is a fragmented market under construction, where players are experimenting a wide variety of strategic moves
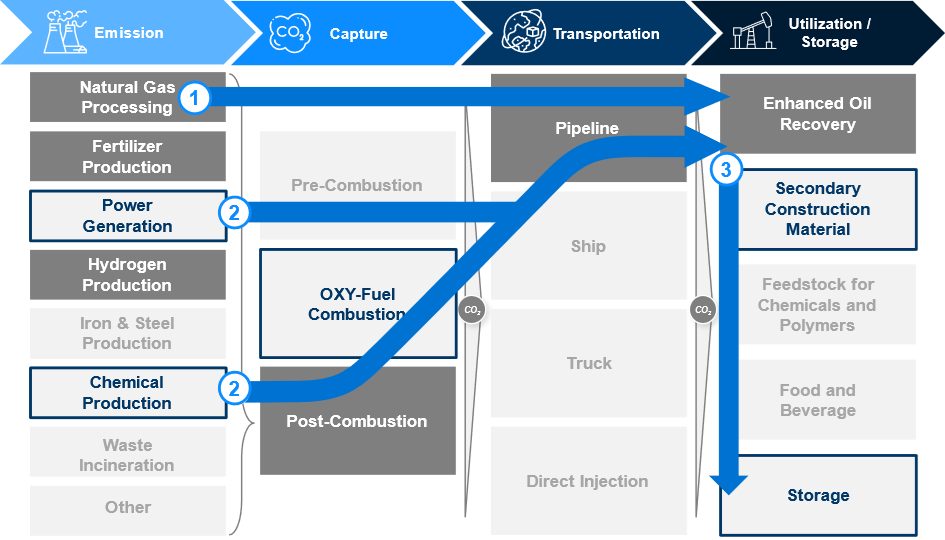
The value chain consists of four distinct steps, currently focused on heavy industries where enhanced oil recovery (EOR) as an end market is profitable.
Currently, the value chain is overweight towards specific sources and techniques with horizontal and vertical movements:
- Established players, such as ExxonMobil, are looking to move horizontally along the value chain to extract value from their CO2 emissions.
- Market players generating CO2 in Power Generation and Chemical Production are entering the market through investment in new carbon capture facilities.
- The market is expected to vertically shift along the utilization component of the value chain. Current end uses for carbon are not as valuable as Enhanced Oil Recovery, but companies are continuing to invest in ways to monetize carbon emissions through other industrial uses.
The conditions for success on the CCUS market
From the value chain analysis, five key success factors can be identified:
- Build capability to identify, characterize and reach out to industrial sites with high CO2 concentration emitters
- Rely on carbon capture technologies that are well developed and limit the cost – learn from established CCUS facilities.
- Build storage sites with accessibility to existing CO2 pipeline infrastructure to minimize transportation costs.
- Develop CO2 product agreements whether it’s or EOR usage or with new markets that emerge as CO2 use cases continue to develop.
- Anticipate, locate & leverage on government incentives to maintain economic feasibility.
However, there are some roadblocks to be considered. These are similar to other emerging markets such as the geothermal energy market:
- Inexperienced industries: compared to mature industries, there is little experience developing CCUS facilities. This results in investors applying a risk premium, significantly increasing the cost of capital required. Further R&D is required to improve process efficiency and to advance the technology.
- Infrastructure needs: retrofitting current technology on various facilities is a difficult and expensive process. Current transportation techniques are underdeveloped and require large infrastructure investments to take advantage of economies of scale.
- Regulatory uncertainty: strong momentum for CO2 regulations exists but have not been adopted globally especially in high greenhouse gases (GHG) areas such as India and China. Safety requirements and liability policy are two aspects that must be clarified, particularly around long-term CO2 storage.
Tangible results at each mission
July 17, 2023
The space industry’s path to a sustainable future
July 4, 2023
Measure R&D performance
June 19, 2023
Standardization perspectives of nuclear plants
June 8, 2023
